what is australia relative location to new zealand
12.one Introducing the Realm
Learning Objectives
- Summarize how colonialism has affected the development and socioeconomic conditions of Australia and New Zealand.
- Determine where the Wallace Line and the Weber Line were located. Sympathize how isolation has allowed for the loftier level of biodiversity.
- Outline how colonialism impacted the Maori and the Aboriginal populations.
Isolation Geography
Effigy 12.2
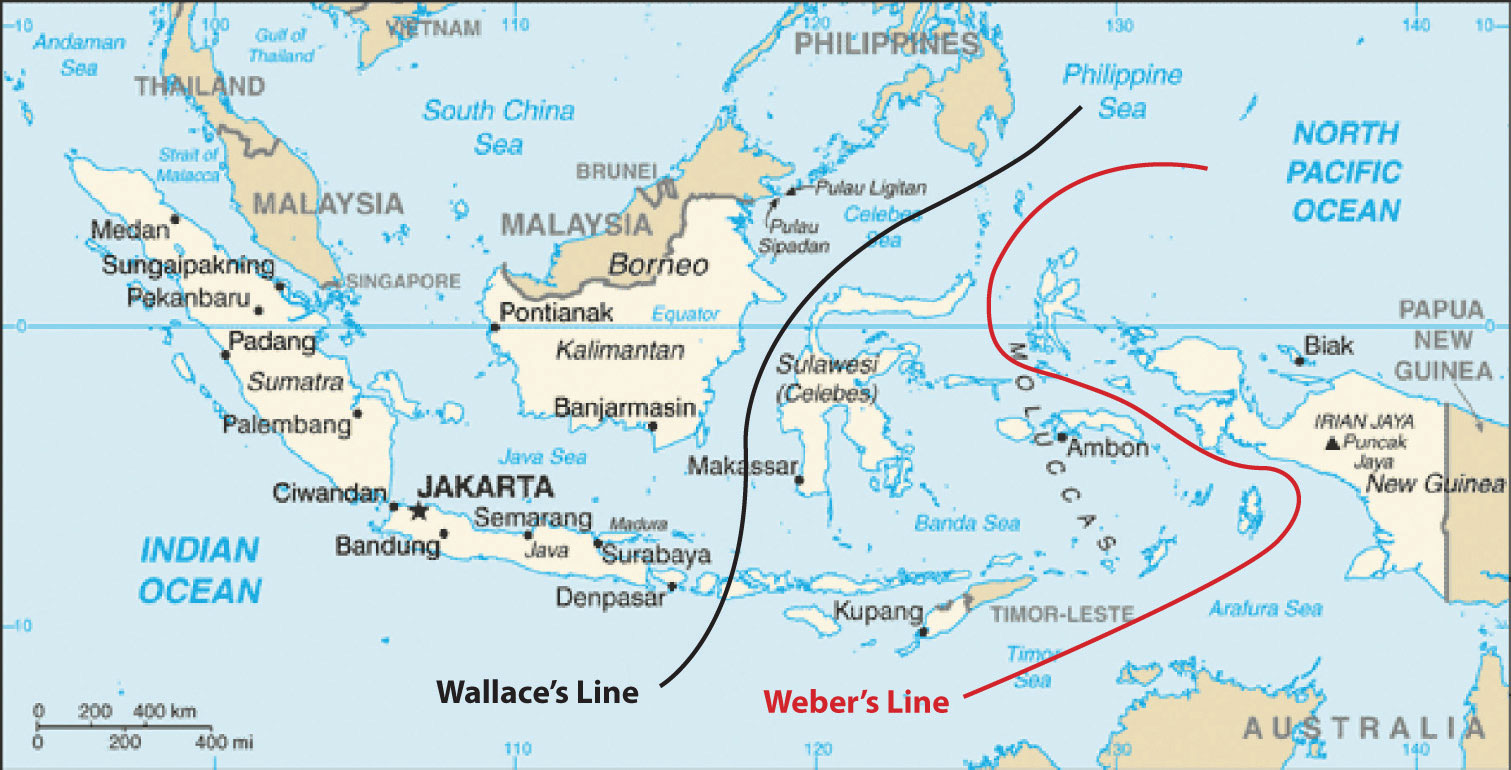
Wallace's and Weber's Lines were developed independently to account for the differences in biodiversity between the Austral realm and the Asian realm. Scientists keep to analyze the true boundary betwixt the realms. These lines demarcate a articulate environmental difference in species development between the two sides.
Source: Updated from map courtesy of CIA World Factbook.
The celebrated isolation of New Zealand and Australia from the rest of the world has caused animals and organisms that are not institute anywhere else to develop in these two countries. The unique biodiversity includes marsupials, or animals whose young are raised in the mother's pouch, such as kangaroos, wallabies, koalas, and bandicoots. It is believed that these creatures developed separately after the continents broke away from each other more than two hundred million years ago. Many plant species are besides unique to this realm. The biodiversity found here is carve up from that of Asia. This has been explained past various biogeographers by cartoon imaginary lines just north of Australia to indicate the line of division between the Asian realm and the Austral realm. Wallace's Line and Weber'south LineImaginary lines fatigued on a map through Indonesia demarcating the separation of plants and animals between the Asian realm and the Austral realm, which accounts for the uniqueness of the flora and fauna of Australia and New Zealand. are two such examples. Both examples attempt to plant the correct line of demarcation for the differences in species evolution between the two sides. During the ice ages, sea level was lower, and the many islands of Southeast Asia were continued by land to the mainland. Papua New Guinea was continued to Australia. Wallace and Weber believed that no land bridge connected the Asian side with the Austral side for animals to cross over. This separation acquired the organisms to the due south to develop independently of those in the north. For example, marsupials are not institute on the Asian side of these lines but are institute on the Australian side.
Colonialism
New Zealand and Australia were both inhabited before the era of European colonialism. Ancient people are said to take migrated to Commonwealth of australia across Southeast Asia from the mainland of Asia more than twoscore grand years ago. They fabricated Australia their dwelling house and adjusted to the physical geography of the continent. For tens of thousands of years earlier the Europeans arrived, the Aborigines carved out an existence in Commonwealth of australia and developed their cultural ways. Only about four hundred l thousand Aborigines remain in Commonwealth of australia today. New Zealand was inhabited past the Polynesian group called the Maori who established themselves on the islands in the tenth century. For hundreds of years they, too, established their culture and traditions in the region before the Europeans arrived. The Aborigines in Australia and the Maori in New Zealand were both confronted with the European invaders. From their standpoint, at that place was much to lose by the arrival of the Europeans. Lands were lost, new diseases killed many, and control of their methods of livelihood were taken over by Europeans. The Maori initiated a number of wars against British colonizers, merely in the finish the greater military power gained the advantage. At the nowadays time, the Maori make up less than 10 per centum of the population of New Zealand.
The sighting of Australia by the Dutch dates to 1606. Portuguese explorers may take discovered Australia earlier, just there are no written records. In the early 1700s, the northern and western coastlines of Australia were known as "New The netherlands." There were no established colonies. James Cook, a naval officeholder working for the British navy, allowable the proficient transport Endeavor and mapped Commonwealth of australia's eastern declension in 1770. He made port at Botany Bay, only s of the current metropolis of Sydney and claimed the region for Britain. He named the country New South Wales. The charting of the coast resulted in continued attention being paid to the region.
Meanwhile, England had a severe trouble with overcrowding of its prisons. Its trouble was exacerbated by the loss of Britain's American colonies. Upon Cook's return to England, interest was generated in the concept of relieving prison house overcrowding by sending prisoners to Commonwealth of australia. In 1787, 11 ships with seven hundred fifty convicts sailed from Slap-up United kingdom of great britain and northern ireland to Phytology Bay. Prison colonies were established in Commonwealth of australia. By the end of the seventeenth century, the entire Australian continent was nether the British Crown. At the same time that the movement of prisoners from England to Commonwealth of australia was diminishing, the next wave of immigration was being fueled by the discovery of gold in the 1850s. The practice of transferring prisoners to Australia ended in 1868. The arrival of the Europeans had caused a serious demise in the Aboriginal population. Aborigines were completely decimated in Tasmania.
Figure 12.3
Slap-up Britain colonized Australia by establishing prison colonies. The prison house colony of Botany Bay was located well-nigh the current metropolis of Sydney, Australia.
In 1901, the diverse territories and states of Australia came together under one federation called the Republic of Australia. A new federal capital letter city of Canberra was proposed. By 1927, Canberra was ready for government activity. This republic regime even so immune for individual state differences. The British monarch is considered the head of state, though it is mainly a formalism position. There have been movements within Australia in recent years to separate from the British Crown, but they have non been canonical. Commonwealth of australia has a democratically elected government.
British naval officer James Cook mapped the coastline of New Zealand in 1769. As the colonial era emerged, Dandy U.k. took possession of New Zealand and included it with its colony of New Southward Wales. In the 1840s, New Zealand became a carve up crown colony. The colony adult a local parliament and a representative government. By 1893, New Zealand made headlines as the commencement country in the world granting all women the right to vote. As a part of the British Empire, the country was made a commonwealth nation in 1947 and has been functioning independently ever since.
Cardinal Takeaways
- Australia is an island continent that was dwelling to ancient people who accept lived there for tens of thousands of years. The British colonized Commonwealth of australia past first creating prison house colonies for convicts from Not bad Britain.
- New Zealand has ii chief islands and is home to the Maori, who were originally from Polynesia. The British colonized New Zealand and often were in conflict with the Maori.
- Australia is relatively apartment with low elevation highlands and an extensive dry interior, while New Zealand has loftier mountains and receives adequate rainfall.
- The Austral realm was isolated past concrete geography. Weber'south Line and the Wallace Line were attempts to distinguish the location of the separation between biological environments.
Discussion and Study Questions
- For what purpose was Australia showtime colonized? What European state colonized Australia and New Zealand?
- How did the colonial activity touch on the indigenous people?
- How is the Austral realm isolated from the rest of the globe?
- Who are the main indigenous people of New Zealand and where did they originally come up from?
- Explain how the colonial development of Australia was like to the colonial development of the U.s..
Geography Practice
Identify the following primal places on a map:
- Arafura Ocean
- Cape York
- Coral Body of water
- Cracking Australian Bight
- Keen Barrier Reef
- Gulf of Carpentaria
- New South Wales
- Sydney
- Tasman Sea
- Tasmania
- Timor Body of water
12.2 Australia
Learning Objectives
- Summarize the colonial exploitation and development of Australia.
- Empathize the basic characteristics of Australia's physical geography.
- Outline how the core-periphery spatial relationship applies to Australia.
- Describe the country's general cultural attributes.
- Summarize the methods used for the country to proceeds national wealth.
Concrete Geography
There is an international attraction to the island continent of Commonwealth of australia, and the attraction has grown in intensity in the past few decades. Tourism is at present the number i economic activeness in Australia. But slightly smaller in physical surface area than the continental United States, Australia is a large country with many resource but few people relative to its size. The Tropic of Capricorn runs correct through the middle of this country. Commonwealth of australia hosts many unique species of plants and animals, including marsupials and a host of poisonous snakes and insects. With the appearance of European colonialism, new species were introduced to the country, which regrettably caused the extinction of some of the native species merely also gave Commonwealth of australia a wide multifariousness of organisms and natural conditions.
Australia is a relatively low-lying island with low relief. Information technology is the flattest of all the continents. The various highland ranges are pronounced, but are non high in elevation. The Smashing Dividing Range is a mountain chain extending from Melbourne in the s to Greatcoat York in the north. This low-lying range of highlands averages about four one thousand feet and reaches an pinnacle of just over 7 thousand anxiety at its highest peaks in the south. The largest river in Australia is the Darling-Murray River system that starts in the highland of the Not bad Dividing Range and flows inward through New Southward Wales, Queensland, Victoria, and South Australia.
The nifty interior of the state is domicile to the massive outback. Extending west from the Great Dividing Range, the outback encompasses most of the interior. This region receives less rainfall than along the declension and its terrain consists of deserts and semiarid plateaus with rough grasses and scrublands. The outback is sparsely populated, but is domicile to a number of ancient groups. Many of the school-age children in the outback accept traditionally received their school lessons through television or radio broadcasts because of their isolation. Mining and some agricultural activities tin be found in the outback. Alice Springs is located in the center of the continent and has been given the designation of the middle of nowhere, or the heart of everything.
Effigy 12.4 The Ghan (Train) Waiting at Alice Springs Station before Continuing N to Darwin

The remote town of Alice Springs is located at the center of the Australian outback.
The deserts of Australia's interior make up a large portion of the continent. Western Australia has iii large deserts: the Gibson Desert, Great Victoria Desert, and Nifty Sandy Desert. The Simpson Desert is located in the border region betwixt the Northern Territory, Queensland, and South Australia. These deserts are not all sand; course grasses and various species of spinifex, a short plant that grows in sandy soil, as well grow in the deserts. The Cracking Artesian Basin on the western border of the Swell Dividing Range receives very picayune rainfall. Information technology would be classified every bit a desert merely for its underground water resources, which support extensive farming operations. Large livestock businesses be in Australia'due south interior with massive herds of cattle and sheep. The grassy plateaus and scrublands provide grazing for domesticated livestock and fifty-fifty wild camels.
The Smashing Barrier Reef, the largest bulwark reef in the earth, extends for 1,600 miles off the northeastern coast of Australia. It is habitation to a host of sea creatures and fish that draw millions of tourists each twelvemonth. The reef attracts scuba divers and water enthusiasts from around the earth. The reef is a main tourism attraction and brings income to the Australian economy. The Great Bulwark Reef has been designated every bit a United Nations Earth Heritage Site. Brisbane is located on the Golden Coast, which gets its name from the cute sandy beaches. The beaches attract an important tourism market for the country.
Figure 12.5 Aerial view of Uluru (Ayers Rock), Located in the Interior of Australia about Alice Springs
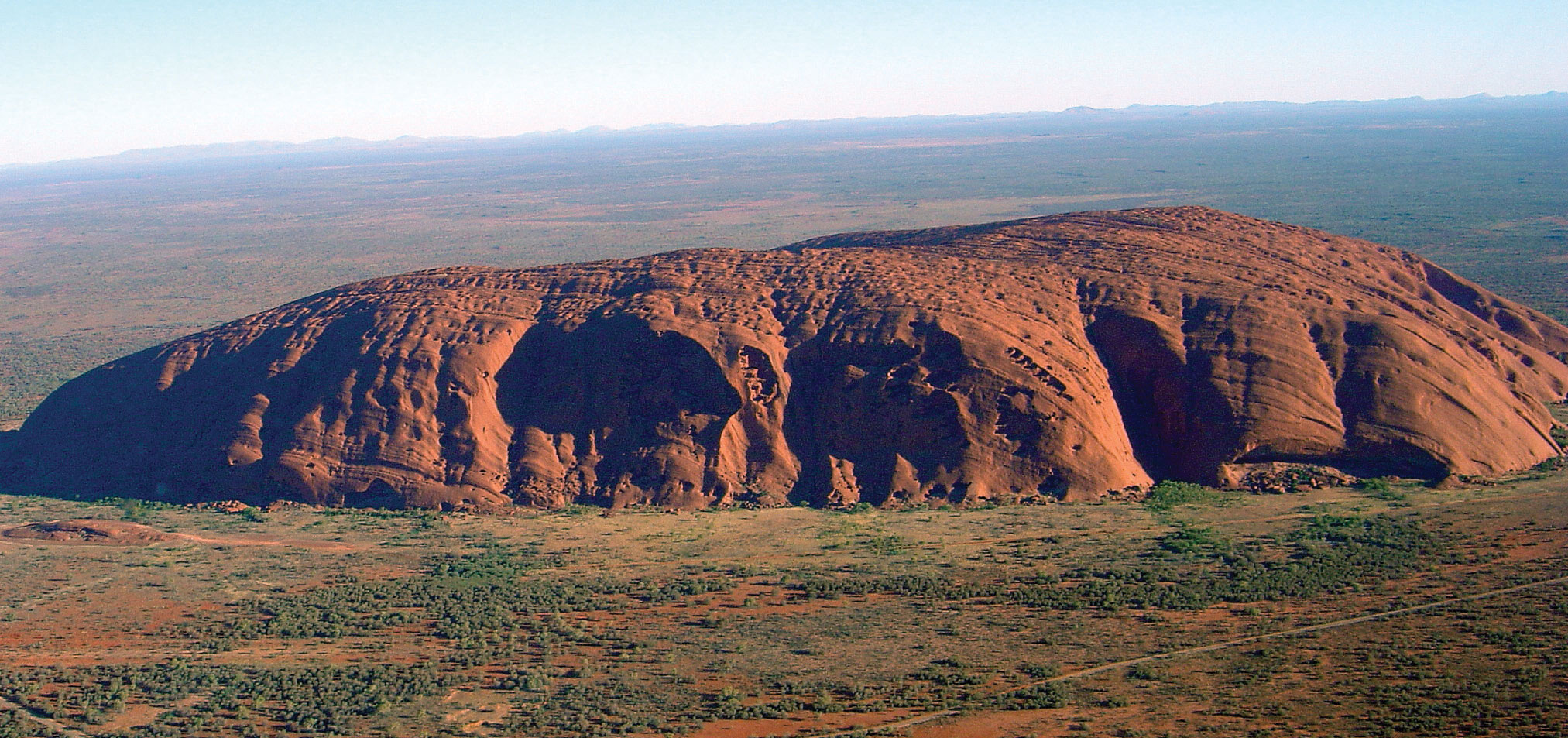

The rock rises i,142 feet above the outback and is two.2 miles long. The site is sacred to the Aborigines and is a major tourist allure. It is listed as a Globe Heritage Site.
A couple of large physical features of interest and significance to Australia are the two largest monoliths in the world. In western Commonwealth of australia, more than than 5 hundred miles to the northeast of Perth, is Mt. Augustus National Park, which features the rock known as Mt. Augustus. It is considered to be the largest single rock in the earth. Mt. Augustus rises 2,352 feet to a higher place the desert landscape. The single structure is most five miles long. Mt. Augustus is more than than twice the size of the about famous Australian monolith of Uluru (Ayers Rock). Uluru is located about two hundred miles southwest of Alice Springs in the Northern Territory and is a well-known tourist allure. Uluru rises one,142 anxiety above the outback and is about ii.ii miles long. Both rocks hold significant cultural value to the aboriginal populations in Commonwealth of australia. They both take ancient petroglyphs, and both are considered sacred sites. Uluru has been more popularized through tourism promotions.
Climate Regions
Central and western Australia are sparsely populated. Large areas of the Northern Territory and the desert regions are uninhabited. Approximately 40 percent of Australia's interior is desert, where Type B climates dominate. The large land mass can oestrus upwards during the summertime months, triggering high temperatures. Depression humidity allows heat to escape into the atmosphere afterwards the lord's day goes downwards, so there is wide temperature variation between day and night.
Along the northern coastal region there are more tropical Type A climates. Closer to the equator and with the sea to moderate temperatures, the northern areas around Darwin and Cape York have little temperature variation. Temperatures in Darwin average virtually 90 °F in the summer and 86 °F in the winter. Spring monsoons bring additional rainfall from February to March.
Tasmania, Victoria, and the cadre region of the southeast take a more moderate and temperate Type C climate. The principal cities, such equally Sydney, Melbourne, and Adelaide, are within this area. Information technology is not surprising that in that location is a straight correlation between Type C climates and the major population areas. The Tropic of Capricorn cuts across the continent, indicating that the cities are not that far south of the tropics. Average wintertime temperatures in June and July exercise not usually fall beneath fifty °F and average summertime temperatures in January and February remain around 70 °F. Since the seasons are reversed from that of the Northern Hemisphere, many Australians go to the embankment for Christmas.
Figure 12.6 Australia's Provinces and Territories and Their Corresponding Major Cities
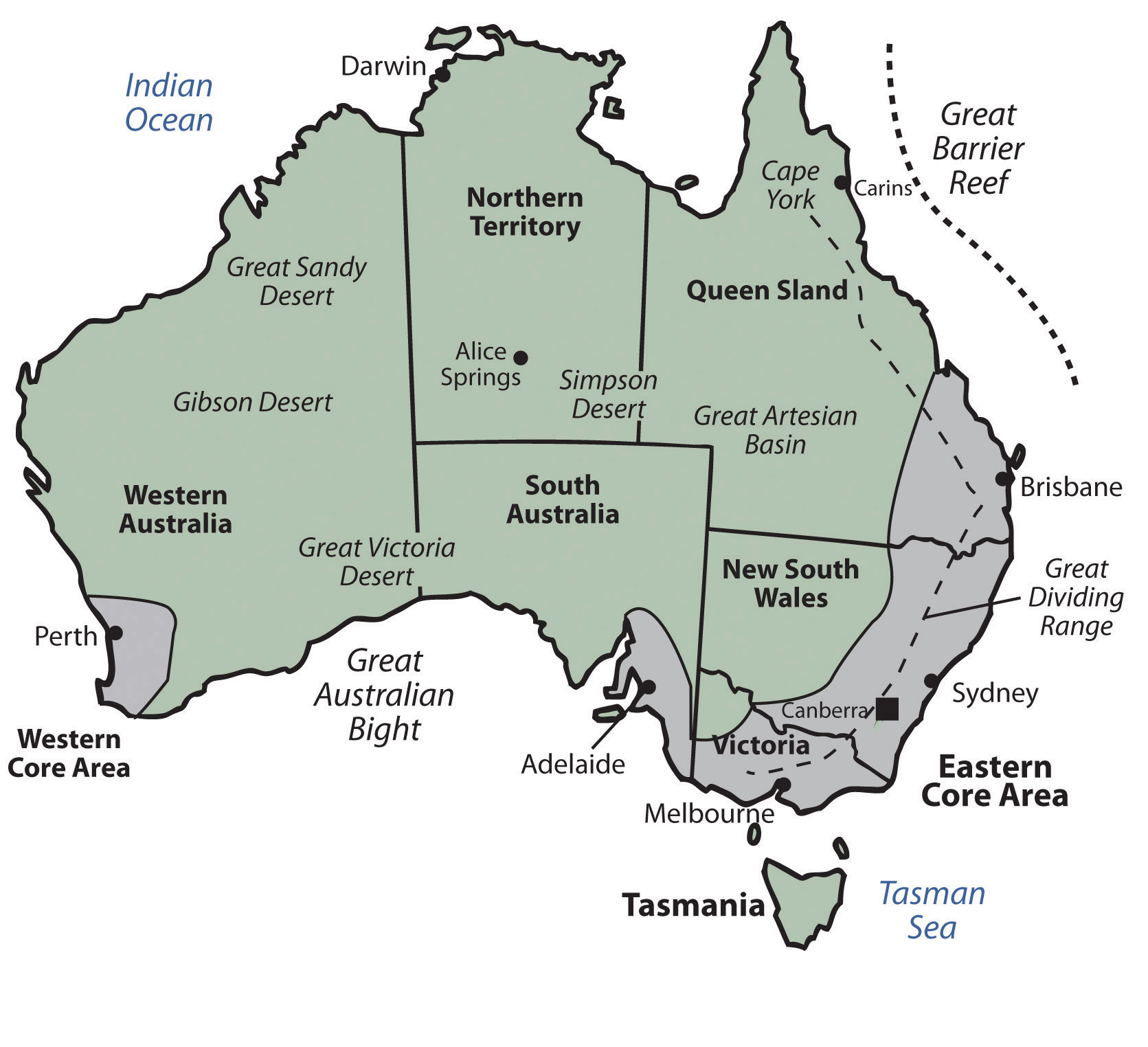
The two cadre areas, where about of Australia'due south population resides, are too noted. Not unexpectedly, the cadre areas take a dominant type C climate, following the full general principle that humans gravitate toward type C climates.
Population, Urbanization, and the Core-Periphery Spatial Human relationship
Australia is divided politically into half-dozen states and two territories. They are the Northern Territory, Australian Capital Territory, Western Australia, Tasmania, South Commonwealth of australia, Queensland, and New Southward Wales. Australian protectorates are composed of a number of pocket-size islands around Australia. Australian core areas are conducive to large human populations. To locate the core population areas in Australia, simply notice the moderate Type C climates. Australia has 2 core regions. There is a pocket-size core region in the west, anchored by the city of Perth. Most of Australia's people live in the large core region in the eastward forth the coast. This region extends from Brisbane to Adelaide and holds most of the land's population.
The total population of Commonwealth of australia in 2010 was only virtually 20-two million. There are more people living in Mexico City than in all of Commonwealth of australia. More than 90 percent of this population has European heritage; about of this percentage is from the British Isles. English is the dominant language. Christianity is the dominant organized religion of choice. The makeup of the people is a production of European colonialism and clearing.
Only well-nigh 2 percent of the electric current population consists of Ancient people, the original people of Australia. Australia's population has seen periodic growth spurts equally waves of immigrants responded to national policies encouraging immigration. This was particularly true after World War 2. About 24 percent of the current population was born exterior Australia; nearly come from the United Kingdom, and some other big per centum comes from New Zealand. Asian countries have also contributed to the Australian population, with measurable numbers of immigrants from China, Vietnam, and the Philippines. And lastly, people from Italy and India also make up a notable proportion of Australia'southward immigrant population.
Commonwealth of australia'southward population is not spread evenly across the mural, since a large portion of the country is desert. The population is concentrated mostly in the urban areas. Virtually xc percent of the population inhabits the cities, which are more often than not in littoral areas. The largest city, Sydney, is often referred to as the New York of Australia. Sydney is positioned at the centre of the main core expanse, the land of New South Wales. To the south of Sydney is the Australian Capital Territory, abode to the capital letter city of Canberra. Other major Australian cities include Melbourne, Perth, Adelaide, and Brisbane. Hobart is the largest city on the island of Tasmania and Darwin is the largest city in the Northern Territory.
Figure 12.7 The Sydney Opera Business firm Viewed from the Water with the City Skyline
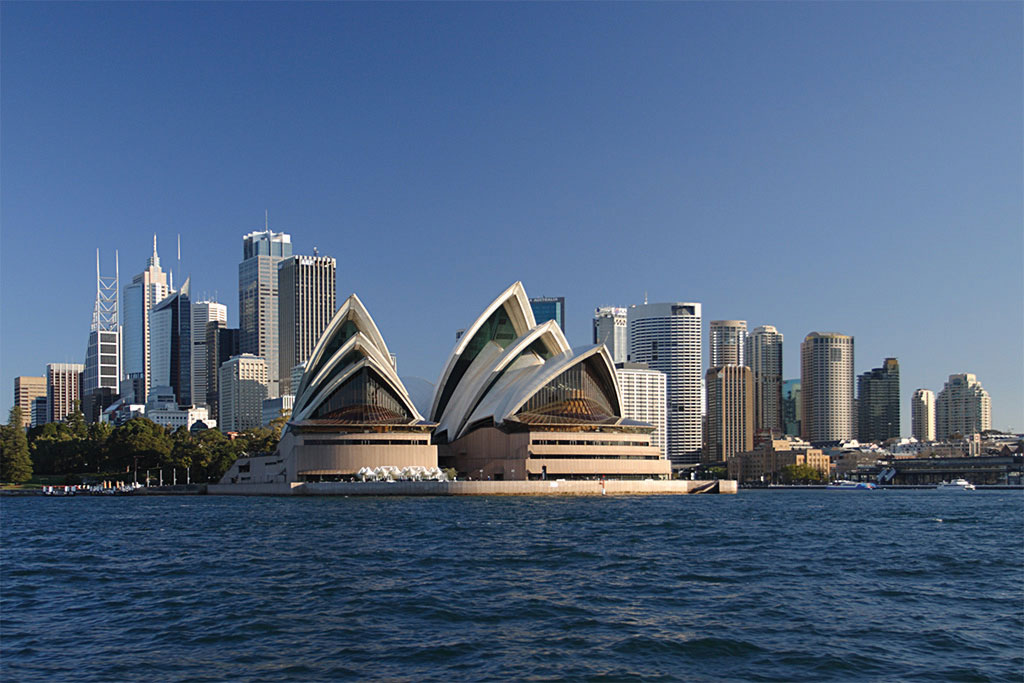

All the large cities of Commonwealth of australia—with except the planned capital city of Canberra—are located on the coast. This blueprint of urban distribution was a product of European colonial development. Most of Australia's population lives in the two economic core regions, then Australia exhibits a distinct cadre-periphery spatial design. The core areas concord the ability, wealth, and influence while the periphery region supplies all the food, raw materials, and goods needed in the cadre. Australia has never had a majority rural population since its Aboriginal times. In that location has been picayune rural-to-urban shift in Australia's population. This is similar to Japan's urban development pattern.
English is the kickoff language of the vast majority of the population. Recently enacted policies and irresolute attitudes toward multiculturalism have spurred growth in the number of immigrants and their descendants who speak 2 languages fluently—English and the language of their birthplace or national heritage. Indigenous languages have not fared so well. As many every bit three hundred indigenous languages were spoken by AboriginesPeople native to Australia when the European colonialists arrived. earlier the Europeans arrived, and merely a few hundred years afterwards, that number now stands at about seventy. About aboriginal languages are in danger of dying out.
Culture and Immigration
Until 1973, Australia had a collection of laws and policies known every bit the White Australia policy, which served to limit the clearing of nonwhite persons to Australia. While the White Commonwealth of australia policies limited immigration from some areas, other policies sought to expand immigration from the U.k.. Subsidies were offered to British citizens to relocate to Commonwealth of australia. Betwixt 1830 and 1940, more than than a million British citizens took advantage of the offering.
Recent census data indicate that about a quarter of the population identifies itself as Roman Catholic and another 20 percent self-identifies as Anglican (the national faith of the United Kingdom). An boosted 20 percent self-identify as Protestant, other than Anglican, and well-nigh 15 percent as having no religion. Regular church attendance is claimed by at about 7.v percent of the population. Despite mod Commonwealth of australia having been settled by the British, Australian law decrees that Australia will have no national organized religion and guarantees freedom of organized religion.
Sports are an important part of Australian civilisation, maybe attributable to a climate that allows for twelvemonth-round outdoor activeness. Virtually a fourth of the population is involved in some kind of organized sports team. Football (soccer) is pop, as is true in most European countries, and rugby and cricket are pop as well. The most popular spectator sport in Commonwealth of australia is Australian Rules Football, as well known as Aussie Rules Football, or but "footy." This uniquely Australian game has codification rules that engagement back to 1858 and is a variant of football game and rugby. Other forms of entertainment include television, film, and alive performances of every kind. Although Australia has a number of its ain tv stations, there are concerns that pop civilization is showtime to be dominated past American influences. Commonwealth of australia'south large cities take extensive programs in the arts. Sydney is becoming a center for world-course performances in trip the light fantastic, opera, music, and theatre.
Education is well funded and internationally respected. School attendance is compulsory between the ages of six and xv, and the adult literacy rate has held steady at nearly 99 percent. Almost students attend publicly funded schools, which are secular. Private schools, which charge tuition fees, do exist and are typically run by religious organizations, predominantly the Cosmic Church.
Economical Geography
Nigh of Australia—peculiarly the wide expanse of the arid interior known as the outback—has immense open spaces, agricultural potential or excellent resources extraction possibilities. The extensive grasslands support tens of millions of domesticated animals—mainly cattle and sheep—which accounts for up to one-5th of the world'due south wool production. Large agricultural businesses include thousands of acres under one operation. The western sector of the Neat Dividing Range in New S Wales is an splendid region for commercial grain operations. The littoral region in Queensland, since it is warmer and receives more rainfall, is adept for sugarcane and similar crops. Sheep and cattle ranches are common in cardinal Queensland and Western Australia. Various regions of southern Australia are first-class for grape and fruit production. Australian wine production has risen to compete with the United states of america and European markets. Only the dry fundamental desert regions in the center of the continent are not favorable for agronomics. In the early on portion of the twentieth century, Australia gained enormous wealth by exporting food products to the remainder of the world. This is even so true, but the turn a profit margin on food appurtenances is no longer what information technology used to exist. The country has had to look elsewhere to gain wealth.
Figure 12.8

The agricultural region of the Barossa Valley in South Australia grows grapes and produces vino. Agronomical production is a major source of economic wealth for Commonwealth of australia even though just 11 percent of the population lives in rural areas. Commonwealth of australia's wine production is expanding to compete in the global marketplace, with French republic and California as major competitors.
Australia has excellent food production capabilities. It too has an excellent mineral resources base of operations. Dissimilar types of minerals tin can exist plant in different regions throughout Australia. Western Commonwealth of australia has iron ore mines. The eastern region of Queensland and New Southward Wales has abundant coal reserves. Minerals such as zinc, copper, gilded, silverish, tungsten, and nickel tin can exist plant in various parts of the country, including Tasmania. Oil and gas fields tin can be institute in the northwestern coastal waters and in the Tasman Sea eastward of Melbourne. The country is self-sufficient in natural gas simply does have to import some petroleum products.
Figure 12.9 Commonwealth of australia'south Distribution of Raw Materials
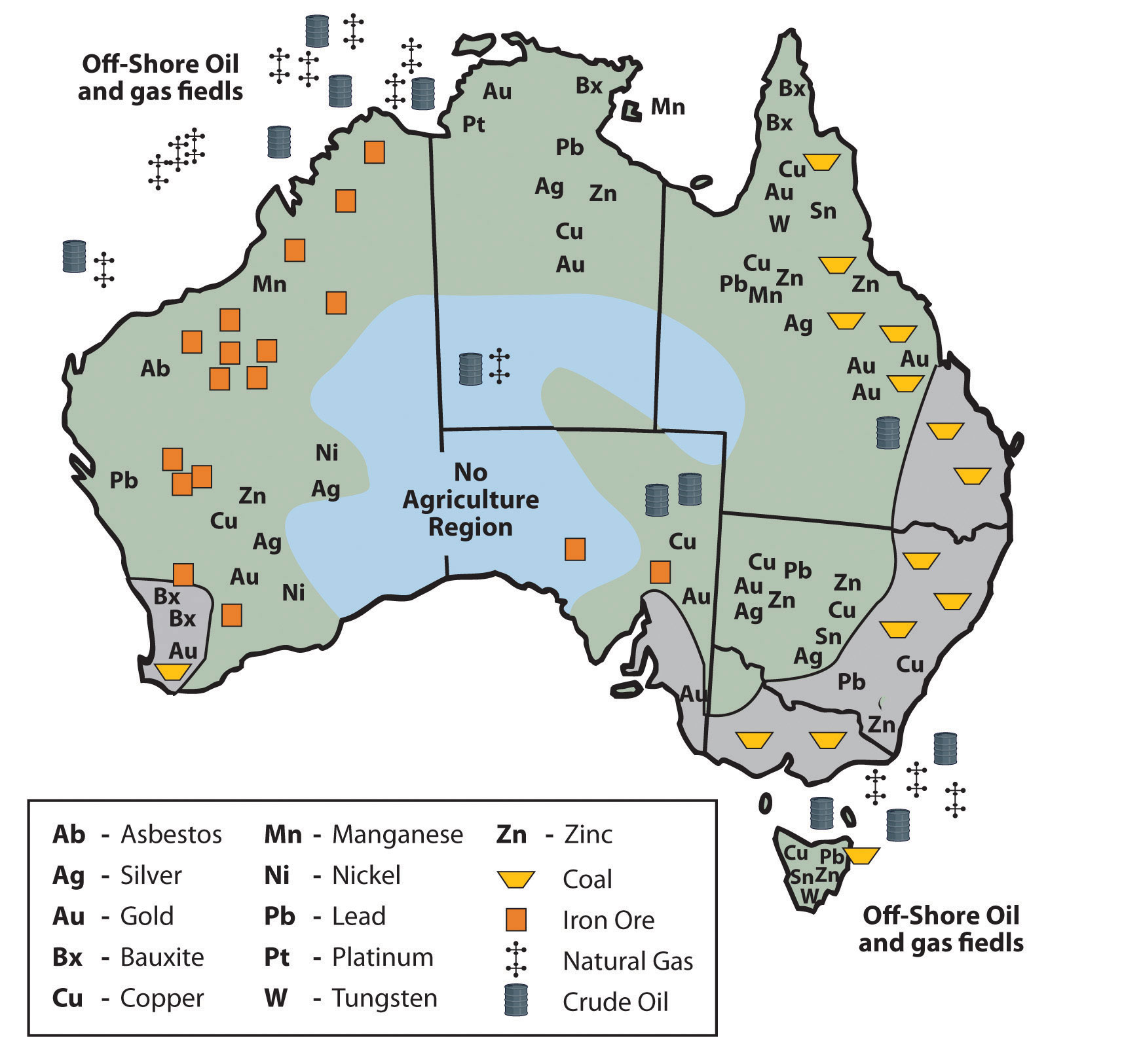
Are any Australian-manufactured products available where yous live? What products can you think of? Australia does not export many manufactured goods. Its main exports are food and raw materials. If yous remember how countries gain wealth, the method with the highest valued-added profit is manufacturing. Think about Japan and the four Asian economical tigers, and how they accept gained their wealth. The economic tigers have few raw materials. Where exercise you lot suppose the economic tigers and Nippon get their raw materials? With Japan'due south enormous manufacturing chapters, it has a high demand for imported iron ore, minerals, and raw materials. Though Australia is a quondam British colony, Cracking U.k. is not considered Australia'southward largest trading partner. Commonwealth of australia is closer geographically to the Asian economical customs than to the European Union. Nippon has go Australia's biggest trading partner. When Commonwealth of australia is viewed in the news, in telly programs, and in Hollywood movies, it is portrayed as a country with a like standard of living to the Usa or Europe. How practice Australians have such a high standard of living if they don't manufacture annihilation for export? To evaluate this, think virtually the size of the population of Australia and consider the distribution of wealth. They export an immense amount of raw materials and have a relatively pocket-size population to share the wealth.
Figure 12.x Bondi Embankment
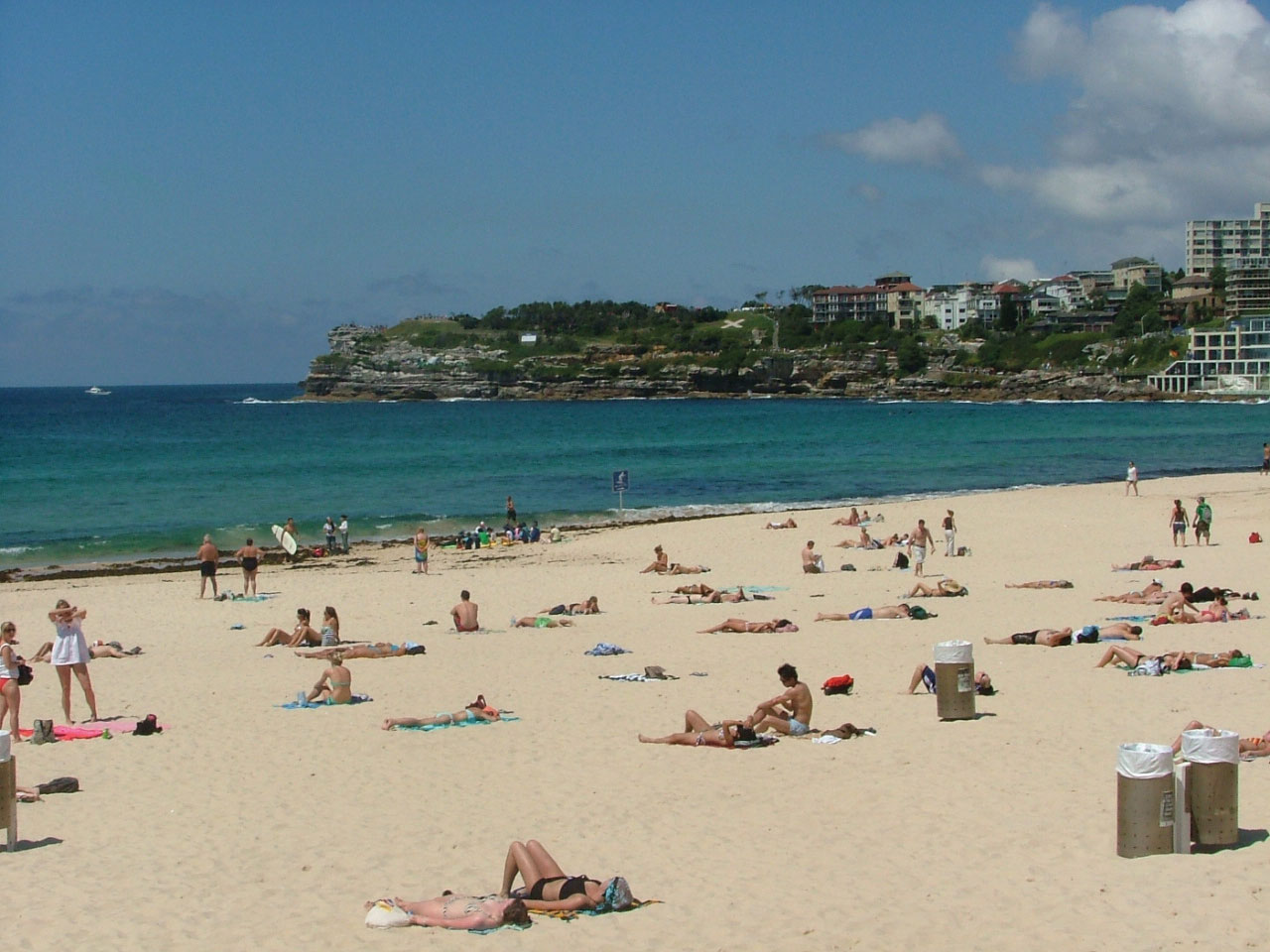

The Gold Declension of eastern Commonwealth of australia draws tourists from the Northern Hemisphere throughout the winter season. It is called the Gold Coast because of the long stretches of gilt sand beaches, the gilt tanned bodies of beach goers, and the high level of income (golden) derived from the tourism industry.
Australia is an bonny place to visit. The environs, the animals, and the culture make it inviting for tourism. Every bit of the year 2002, tourism has become Australia'south number one ways of economical income. From the Corking Bulwark Reef and the Gold Coast to the vast surface area of the outback, Australia has been marketing itself as an attractive identify to visit with peachy success. Tourism from Nihon provides a large percentage of the tourist action. Australia has moved through the initial stages of the index of economic development to become a society that is nigh ninety per centum urban with small families and high incomes.
Mining and Ancient Lands
Territorial command of Australian lands has become a major issue in recent years. Large portions of western Australia and the outback have traditionally been Aboriginal lands. European colonialism on the Australian continent displaced many of the native people. Large sections of country once used by the Aborigines were taken over by the government or by individual interests. Large agricultural operations and mining operations have used the lands without acceptable compensation to the Ancient people who in one case controlled them. Court rulings aimed at reparation for native people have had mixed results.
There are every bit many equally 4 hundred different groups of Aborigines currently in Commonwealth of australia that make up a total population of about four hundred fifty chiliad. This is a small percentage of Australia's population but involves a large part of the physical area of the country. Their land claims include all of the Northern Territory, a large portion of western Australia, and parts of S Australia and Queensland. This is in addition to claims located inside many urban areas, such as the largest city, Sydney. Mining operations on Aboriginal lands have become highly regulated. Concerns accept arisen that Australia's extractive industries will diminish, causing a decline in the economy. The business concern for the Aboriginal population has increased in the past few decades and the regime has made attempts to mediate their political and economic issues besides equally strengthen programs that accost their social welfare.
Australia's Future
The economic future of Australia is circuitous. Though tourism has get a viable ways of providing income, Australia must import manufactured products that it does not produce locally, including electronic appurtenances, computers, and automobiles. Import dependence has increased its merchandise arrears. Trade agreements and protectionism have get a part of the economic puzzle of how to sustain a competitive standard of living. Australia is located next to the Asian realm. Its economic system, civilisation, and future are condign more Asian. Immigration has been an issue in that the regime has always restricted immigration to ensure a European majority. Millions of Asian people would like to migrate to Australia to seek greater opportunities and advantages, but they are legally restricted. It is becoming more than difficult for Australians to concord to their European connections with such an Asian presence. How the state will handle this state of affairs in the futurity will show interesting.
Fundamental Takeaways
- Australia is an island continent that was abode to aboriginal people before the British colonized it past first creating prison colonies for convicts from United kingdom of great britain and northern ireland.
- Australia is a relatively flat continent with low elevation highlands, including the Not bad Dividing Range forth its eastern coast. The interior outback lacks precipitation and has numerous deserts.
- Two master core areas exist where Type C climates prevail and where nigh of the population lives: a large cadre area on the southeastern coast and a small core area effectually Perth on the western coast. The sparsely populated outback makes up the vast periphery, which has large amounts of mineral and agronomical resources.
- Aboriginal people were in Australia for forty thou years. The British colonial activity didn't heat upward until the tardily 1700s. Today, most of the xx-2 million people are from the British Isles and Europe. Merely almost 4 hundred fifty thousand Aborigines remain.
- Commonwealth of australia has few manufacturing enterprises for export profits. Tourism has become the number one method of gaining wealth, with the consign of raw materials the 2d-largest method.
Word and Written report Questions
- Name the European land that colonized Australia. What was the original reason for colonizing Australia?
- What are Australia'southward main political divisions? What is the vast interior chosen?
- What are some of Australia's main physical features? How are they developed for tourism?
- What are the master climate types in Australia? How does climate relate to population?
- What type of government does Australia take? What is its capital metropolis? Who is head of state?
- Outline the cadre-periphery relationship in Australia. What distinguishes the core areas?
- How does Commonwealth of australia compare with the Asian economic tigers? How do they support each other?
- How does Australia maintain a high standard of living when it exports few manufactured products?
- What are Australia'south master exports? Who is their principal trading partner?
- What stage is the land in with regard to the index of economic evolution?
Geography Exercise
Place the post-obit key places on a map:
- Adelaide
- Arafura Sea
- Australian Capital Territory
- Brisbane
- Canberra
- Cape York
- Coral Sea
- Darling-Murray River
- Darwin
- Gibson Desert
- Gold Declension
- Dandy Artesian Bowl
- Great Australian Bight
- Great Bulwark Reef
- Great Dividing Range
- Slap-up Sandy Desert
- Cracking Victoria Desert
- Gulf of Carpentaria
- Hobart
- Melbourne
- New South Wales
- Northern Territory
- Outback
- Perth
- Queensland
- Sydney
- Simpson Desert
- Due south Australia
- Tasman Bounding main
- Tasmania
- Timor Ocean
- Victoria
- Western Australia
12.iii New Zealand
Learning Objectives
- Outline New Zealand's master physical features. Understand how the Due north Island is different from the South Island.
- Empathise how tectonic plate action has helped to isolate New Zealand from the rest of the world and still affects the isle today.
- Summarize the situation of the Maori in New Zealand. Larn well-nigh the Maoris' relationship with the dominant civilization in New Zealand.
- Describe the economic geography of New Zealand and how the land gains wealth.
Figure 12.11 Southern Alps, New Zealand

Physical Geography
To the e of Commonwealth of australia beyond the Tasman Sea is the country of New Zealand. New Zealand is one of a number of sets of islands that make up Oceania, also referred to as the Pacific Islands, a region occupying the western and fundamental Pacific Ocean. The Pacific Islands region is generally divided into 3 subregions: Federated states of micronesia, Melanesia, and Polynesia, with New Zealand being part of Polynesia. The Pacific Island region includes more than than twenty-five g individual pocket-size islands representing xx-five nations and territories. Most of these islands are very small. The South and Northward islands of New Zealand are the 2nd- and 3rd-largest islands, respectively. The N and S Islands of New Zealand are separated past a trunk of water known as the Melt Straight, which is only well-nigh thirteen miles wide at its narrowest point. The Northward and South Islands together are about the same size as the United states state of Colorado. New Zealand also includes a number of smaller nearby islands.
New Zealand, similar Australia, is in the Southern Hemisphere, which means that its seasons are expressed at the opposite times of the seasons in Northward America. In other words, the warmest summer months are January and February and the cooler winter months are June and July. New Zealand lies within the Temperate Zone. In that location are only very moderate seasonal differences, which are slightly more pronounced in the inland areas because the inland areas lack the moderating influence of the ocean. In general, the North Island has somewhat warmer average temperatures than the S Island. In summer, average depression temperatures are almost 50 °F, with daytime highs around 75 °F. In the winter months, depression temperatures boilerplate about 35 °F and loftier temperatures are about l °F. The occurrence of more than farthermost temperatures is limited to the mountainous peaks of the Southern Alps. Snowfall is common in these mountainous regions but rarely occurs in coastal regions.
Figure 12.12 New Zealand
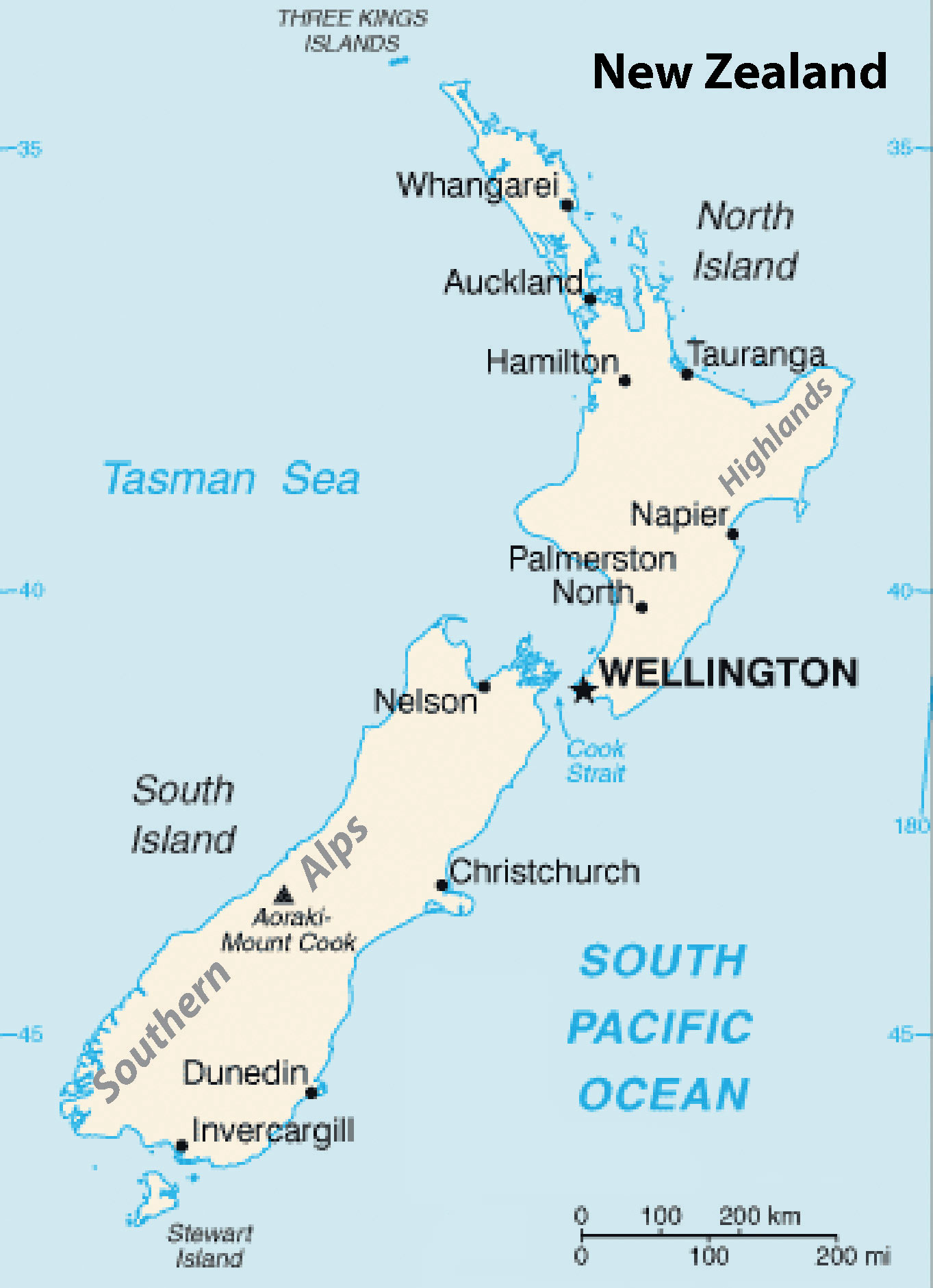
Wellington is the majuscule, Auckland is the largest city in the country, and Christchurch is the largest city on the South Isle. The Southern Alps extend forth the western length of the due south and reach elevations of twelve thousand feet.
Source: Updated from map courtesy of CIA World Factbook.
Rainfall is heaviest on the western coasts of both islands, simply specially on the South Isle. The prevailing westerly winds, carrying wet from the sea, come in contact with the mountains of the Southern Alps and high atmospheric precipitation results. The mountains also have the reverse effect. On the eastern side of the mountains is a rain shadow where the westerly winds accident hot, dry air and the eastern coasts are therefore substantially drier than the western coasts. Therefore, average precipitation rates vary widely across the state. The average almanac rainfall in Christchurch, which is on the eastern coast of the Southward Island, is about twenty-5 inches per year. Auckland, in the midportion of the North Island, receives twice that amount and areas on the wetter western coast receive equally much as one hundred 15 inches per year.
As an island nation, New Zealand's coastlines and oceans are some of its most important geographic features. New Zealand has i of the world'due south largest exclusive economic zones, an oceanic zone over which a nation has exclusive rights of exploration and exploitation of marine resource. New Zealand'due south exclusive economic zone covers more than ane million square miles. The dramatic nature of New Zealand'southward landscape is well known to many moviegoers as the landscape of Middle Earth, as depicted in New Zealand film director Peter Jackson's version of J. R. R. Tolkein's Lord of the Rings.
Tectonic Plates and Gondwanaland
The N Island of New Zealand features a rather rugged coastline with numerous harbors, bays, and inlets. The port cities of Auckland and Wellington are located on 2 of the largest bays. The coastline of the Due south Island is somewhat more regular, except along the southern portion of the eastern coastline, which has deep fjords. Though the North Isle has lower relief than its southern counterpart, its few mountains are volcanic in origin. The two principal islands are accompanied by smaller islands effectually their shores. The North Island's highest superlative is Mt. Ruapehu, which reaches almost 9,175 feet and is an agile cone volcano. It is located in the south primal office of the island. A range of highlands runs along its eastern side. The volcanism associated with Mt. Ruapehu results from New Zealand'southward location atop ii tectonic plates: the Pacific Plate and the Indo-Australian Plate. The purlieus of these two plates forms a subduction zone nether the North Island; consequently, New Zealand experiences tens of thousands of earthquakes per year. Though most of the earthquakes practice not greatly disrupt human action, some have registered higher than vii on the Richter scale. New Zealanders have made use of the geothermal power generated past this and the tectonic features of this area and hence, New Zealand is habitation to several hydrothermal ability plants.
A range of mountains, the Southern Alps, divides the South Island lengthwise. Many of the peaks attain over ten thou feet. The highest summit is Mt. Cook, which reaches college than twelve 1000 anxiety. These mountains are as well formed by the area's tectonic situation. However, the two plates meet in a different way under the Southward Island. Rather than creating a subduction zone, the plates motility laterally. The lateral movement created the South Alps. New Zealand's location places it along one of the edges of the so-called Ring of Fire, which encircles the Pacific Body of water basin. The positions and activity of the tectonic plates in this zone cause most of the world's earthquakes and have formed more 75 percent of the world's volcanoes.
Figure 12.13 The Supercontinent of Pangaea about Two Hundred Million Years Ago
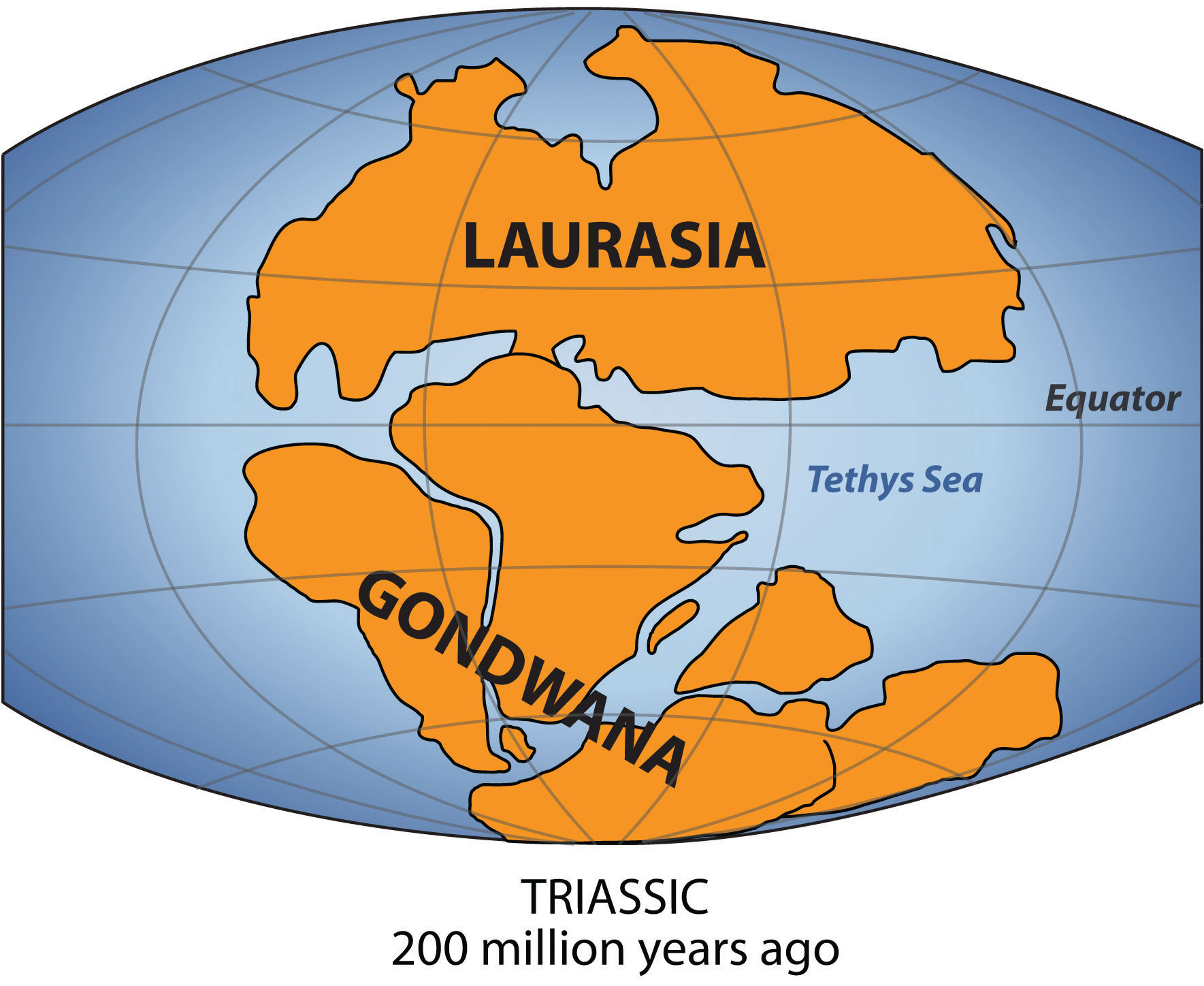
The southern portion was called Gondwana (Gondwanaland). New Zealand and Australia come from Gondwana; their origin explains why their fauna and flora are so unique.
New Zealand has a fascinating ecological history. New Zealand was once office of Gondwana, besides known as GondwanalandPangaea was a supercontinent in very ancient times. Between nigh ii hundred to five hundred one thousand thousand years agone, Gondwana was the southern portion of Pangaea and included most of the land in what is today the Southern Hemisphere. . About two hundred to five hundred one thousand thousand years ago, Gondwana was the southern portion of the supercontinent of Pangaea. Gondwana included nigh of the land in what is the Southern Hemisphere today, including Commonwealth of australia and New Zealand. Over fourth dimension, through various forms of tectonic activeness, the earth's plates shifted and the supercontinent of Gondwana broke apart, leaving New Zealand geographically isolated for millennia. The species of flora and brute constitute in New Zealand either descended from the species found on Gondwana, flew in that location, floated there via the ocean, or were brought by people.
Biodiversity in New Zealand
New Zealand'southward geological history has laid the groundwork for more than 2,000 indigenous plant species, about 1,500 of which are institute nowhere else in the world. The biomes of the North Isle include a subtropical surface area, including mangrove swamps, an evergreen forest with dense undergrowth of mosses and ferns, and a small grasslands expanse in the central volcanic plain. The South Isle biomes include all-encompassing grasslands in the east, which are excellent for agronomical pursuits; forest areas, dominated past native beech copse in the west; and an alpine vegetation zone in the Southern Alps.
In terms of brute, the most influential factor may exist the relative absenteeism of predatory mammals, again related to New Zealand'south geological history. With few ground predators and a favorable climate, bats, small reptiles, and birds were able to thrive and flourish. Without predators, many species of birds became flightless, such as the noted Kiwi. New Zealand's most famous bird, the moa, was similar to the ostrich but is now extinct. Moa could abound to more than twelve anxiety high and weigh more than five hundred pounds. New Zealand is known for its big number of species of wild birds. The Kiwi is the most noted and is often used to refer to people from New Zealand, as it is the national symbol of the state.
New Zealand has a variety of landscapes that accept been bonny for economic activity and tourism. The South Island is larger than the Due north Isle and is more than mountainous. The snowcapped peaks of the Southern Alps run the western length of the Due south Island. Large livestock-raising operations and agricultural activities tin be constitute on the vast grasslands of the South Isle. Millions of sheep and cattle are raised on the grassy highlands and the valley pasturelands. The Northward Isle has more low-lying terrain, which is also skilful for agriculture and is dwelling to a large dairy manufacture. The fundamental highlands of the north offer some rugged relief and provide for a diverse physical landscape.
Cultural Dynamics and the Maori
New Zealand is dwelling house to many Polynesian groups. Its original inhabitants were the MaoriPolynesian people living in New Zealand when the European colonialists arrived. , who came to the islands around the 10th century. They grew crops of gourds and sweet potatoes. Fur seals were hunted regularly, every bit were moa, which were hunted to extinction before the Europeans arrived. The Maori had created extensive trading networks with other island groups and adult a heritage of traditional rituals and cultural means. The Maori civilization thrived for hundreds of years and was well established in New Zealand before the inflow of the colonial ships from Europe.
Britain was the master colonizer of the islands. The British settled in to establish their presence and proceeds control. In 1840, the British colonizers and the Maori signed the Treaty of Waitangi, which granted British sovereignty over the islands but allowed the Maori certain rights over tribal lands. The actual linguistic communication in this treaty has been debated betwixt the English version and the Maori version. Over fourth dimension the tribal lands were codification into legal arrangements by the European colonizers. Since the Treaty of Waitangi, the state of affairs has evolved, with subsequent country exchanges, some legal and others questionable. The Maori take complained about unfair treatment and the loss of land and rights in the process. These issues have finally reached a point of negotiation in the past couple of decades. Starting in the 1990s, treaty settlements take been fabricated to help right the actions of the colonial activity and compensate the Maori for the conditions they were subjugated to.
Figure 12.fifteen A Maori Man with Traditional Topknot and Tattoos
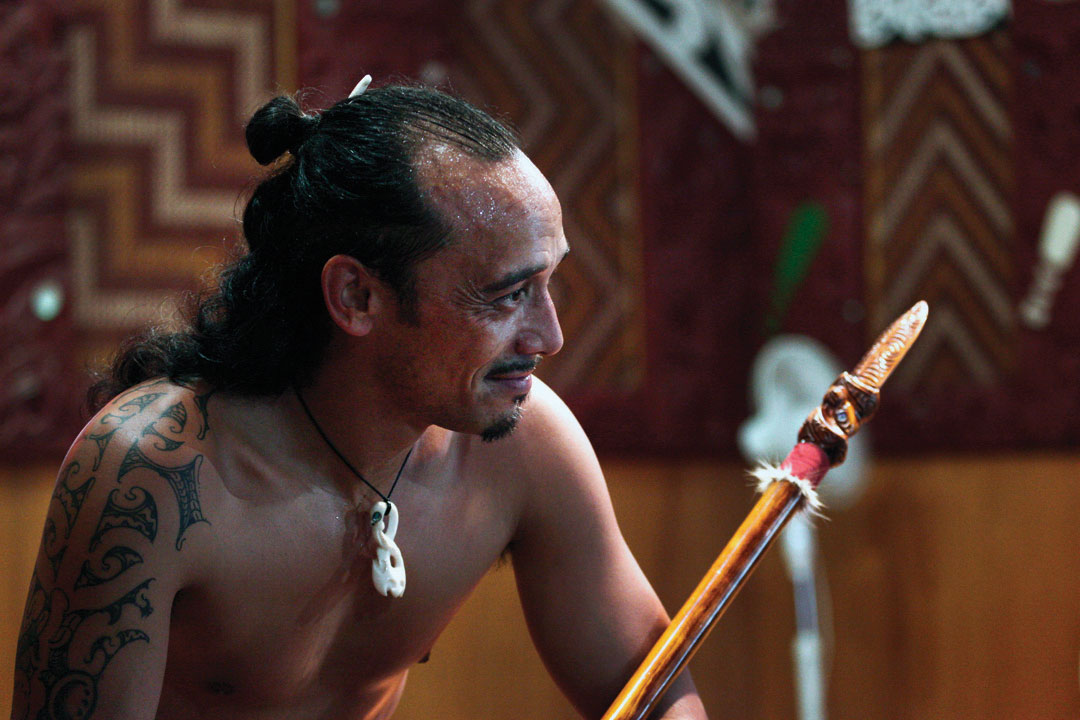

Many Maori participate in performances in New Zealand both for tourism and to maintain their heritage and traditions.
Nigh of the Maori have lived on the North Island. They were a real business organization for the European colonizers. Claimed by Great Britain in their colonial empire, the state of New Zealand became independent of United kingdom in 1901. In 2010, the estimate of the population of the state was at virtually 4.iii one thousand thousand, with Europeans making up 60 pct of the population and the Maori making upwardly about 8 pct. There are also many people who are of mixed ethnic groundwork, including Maori and other groups. Asians, Polynesians, and other ethnic minorities make up the rest. New Zealand's primary religion is Christianity and English is the official language.
The Maori have not been integrated into New Zealand gild to the same extent as Europeans have. The Maori now join the ranks of other Pacific Islanders that take moved to New Zealand from Samoa, Tonga, Cook Islands, and many other places in the South Pacific. New Zealand's urban areas reflect multifariousness in the various cultural landscapes and ethnic communities that have established themselves in specific neighborhoods within the main cities. A common dilemma with all peoples is the draw to return to their heritage and roots, which typically results in a more traditional lifestyle with stronger cultural means. At the same time, the modern world pulls people toward a more global and cosmopolitan civilization that is steeped in modernity with changing fashions. The Maori and other indigenous groups in New Zealand find themselves facing this dichotomy of societal dynamics.
Economic Conditions
Land and climate could be said to be New Zealand's almost important natural resources. Fertile soils and a mild climate, complete with thousands of hours of sunshine annually, create platonic weather condition for agriculture. Grass continues to grow throughout the year, which ways that sheep and other livestock can exist well grazed. Wool and other agricultural products, notably meat and butter, are of import exports for New Zealand's economic system. Salubrious forests produce timber products, which are important to the economy as well. Some of New Zealand's natural resources are establish underground, including coal, natural gas, golden, and other minerals.
Wellington is the upper-case letter of the country and is located on the southern end of the North Island. Wellington is one-fourth the size of the primary urban center, Auckland, which has one.two million people and is located in the north. The major cities are located forth the coastal regions and provide a connection to sea transportation. Christchurch is the largest metropolis of the South Island and is located along the eastern seaboard on the productive Canterbury Plain. The soils and conditions on the Canterbury Plain are first-class for productive agriculture of all types. Coastal plains also provide access to building transportation systems of highways and railroads that are more than costly to construct in the mountainous regions of the Southern Alps or the northern highlands.
The modernistic cities are dwelling to a multitude of processing centers preparing the abundant agronomical products for domestic consumption and for export products. The ever-growing populations of Asia and the rest of the world continue to identify a high demand on nutrient products and welcome New Zealand's agricultural exports. In relation to how countries gain wealth, agronomical profits are usually quite competitive and normally provide a low profit margin. New Zealand does non proceeds a large part of its national income from mining or manufacturing, though these industries do exist. The high standard of living that exists in New Zealand is similar to that of Australia in that the population is not very big, so that the national wealth tin be distributed via the private sector economy to arrange a relatively good lifestyle and provide for a comfy standard of living.
New Zealand has a marketplace economy. The mainstay of the economy is, and has been for many years, a productive agricultural sector that has been geared toward export profits. New Zealand's climate and soils assistance give it a place in the economy of the region through agricultural exports. A "wool boom" in the 1950s furthered the emphasis on agricultural products as tremendous profits accrued in the wool product and consign industry. Today, New Zealand'south economy is yet heavily focused on the export of agricultural products, though the economy has diversified into other areas such as tourism and exploitation of natural resource, especially natural gas. The development of hydroelectricity generation in recent years has been of import to the economy.
Primal Takeaways
- New Zealand has been isolated by the separation of continents through tectonic plate activity. Shifting plates continue to create earthquakes and volcanic activity in the region.
- New Zealand has high mountains, with the Southern Alps along the western coast of the Due south Isle and highlands along the eastern side of the Due north Island. Acceptable rainfall and practiced soils provide for excellent farm production, which has been the traditional economic activity.
- The Maori were established in New Zealand earlier the British colonized information technology. Various agreements were made to piece of work out common arrangements, with varying degrees of success. The Maori keep to be a minority population and have not acculturated into the mainstream society of the land.
- New Zealand has historically relied on agricultural exports for national income. Shifting global markets and changes in authorities policies and structures take highly affected the economic system of New Zealand. The state continues to piece of work its way through the transition to a more global economy.
Discussion and Report Questions
- What are the main concrete features of the Due south Isle and North Island of New Zealand?
- How is the Northward Isle different from the South Island in population and economical activities?
- How has concrete geography been helpful in the economic development of New Zealand?
- Where are the main cities of New Zealand? What are the capital and the largest cities on each island?
- Who were the inhabitants of New Zealand before the colonial era? Where did they come from?
- What issues do these inhabitants of New Zealand have with the electric current government?
- How are the dynamics with the Maori similar to those with the Aborigines in Australia?
- What are the main methods that New Zealand has used to proceeds national wealth?
- How has the economic situation in New Zealand changed over the past few decades?
- How is New Zealand different in physical and human geography from Australia?
Geography Practise
Place the following primal places on a map:
- Auckland
- Canterbury Plain
- Melt Strait
- Christchurch
- Mt. Cook
- Mt. Ruapehu
- Southern Alps
- Wellington
12.4 End-of-Affiliate Cloth
Chapter Summary
- Commonwealth of australia is an independent land and a relatively low-summit isle continent that is distinguished past its large semiarid interior region called the outback. Ii core areas with moderate Blazon C climates along the eastern and western coasts hold almost of the modest population of most 20-two one thousand thousand.
- Great Britain colonized Australia and get-go used it every bit a prison colony. European traditions and heritage prevail, with English equally the chief linguistic communication and Christianity as the main religion. The Aborigines had been there for tens of thousands of years before the Europeans arrived but merely about iv hundred fifty thousand remain.
- The traditional method of gaining wealth in Australia has been through farm production. In the latter half of the twentieth century, the consign of minerals and raw materials became a major method of gaining wealth. In the past decade, tourism has risen to Australia'southward number 1 means of gaining wealth. Concrete features such as the Great Barrier Reef, the outback, and the many unique animals make Australia a destination for world travelers.
- New Zealand is about i,500 miles to the e of Australia across the Tasman Sea. The two main islands of New Zealand have high relief, with the Southern Alps located on the South Island. Moderate climate conditions and acceptable rainfall make New Zealand an highly-seasoned place for agriculture and tourism. The remote locations create an chemical element of isolation that is a price consideration for travel and trade.
- The Maori people from Polynesia inhabited New Zealand before the British colonized it. The Maori had conflicts with the British and, later, the government over the loss of lands and legal arrangements. The Maori brand up less than ten per centum of the 4.3 million people in New Zealand. The Maori situation has common ground with the state of affairs with the Aborigines in Australia, who also have been working to regain land rights and legal settlements.
- New Zealand'southward economical situation has evolved to accommodate international market prices and demands likewise as the internal business and political climate of the country. The primary economic action has been agronomical exports, merely the country has been diversifying into industrial processes and tourism. Natural gas development has besides been expanding.
bertrandtheiropeop.blogspot.com
Source: https://saylordotorg.github.io/text_world-regional-geography-people-places-and-globalization/s15-australia-and-new-zealand.html
0 Response to "what is australia relative location to new zealand"
Publicar un comentario